Problem Definition
Optimizing Hardware for Neural Networks
CPU Architectures
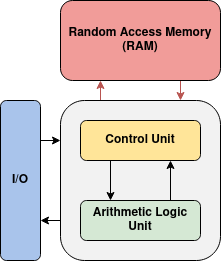
A primary concern when performing machine learning tasks with artificial neural networks (ANNs) is the speed at which inference is performed. On standard hardware that implements a Von Neumann architecture, neurons are evaluated in the central processing unit, called the CPU, while the synapse weight information and neuron outputs are stored in the random-access memory, or RAM. The challenge with this approach is that the transfer of data between the CPU and RAM limits the speed at which the entire network can be evaluated. This is known as the memory bottleneck since the latency of transmitting data between the CPU and RAM bottlenecks the overall performance of the network. Furthermore, the inherent parallelism of the neural network is not able to be realized since the CPU has a limited number of cores that are able to concurrently update the values of the neurons.
GPU Architectures
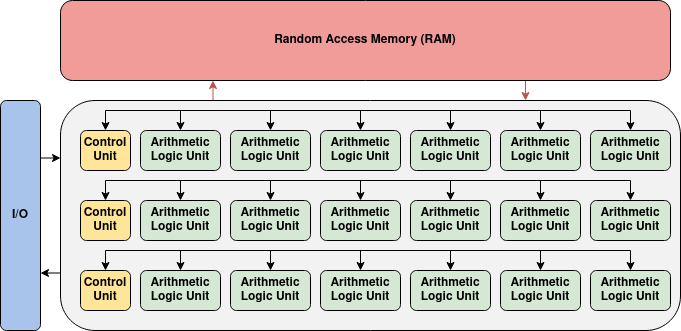
Graphics processing units, or GPUs, have been able to improve the speed of neural networks because of their capability to perform large scale matrix multiplication operations. However, GPUs suffer from high power consumption and like the simpler CPU and RAM model, their hardware layout does not resemble that of a neural network.
Neuromorphic Architectures
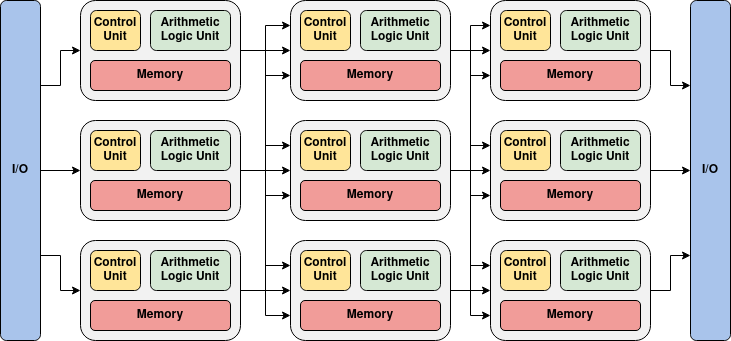
To address these issues, researchers have looked towards the development of neuromorphic hardware to accelerate the speed of both neural network inference and training. Neuromorphic hardware attempts to more precisely model the architecture of a neural network by featuring computing units that correspond to the neurons in the network, and by providing in-memory computing capabilities. By following this approach, the hardware is capable of achieving lower power consumption and faster training and inference times. These custom neuromorphic architectures also make the hardware more scalable in terms of both power and area.
ANN Hardware Performance Issues
As discussed, custom neuromorphic hardware is ideal for improving the execution speed and power consumption of neural networks, however, researchers are also beginning to question the behavior of the traditional ANN model itself. Although neuromorphic hardware accelerates the speed of ANNs, multiplier circuits on the hardware are still slow operations, which occupy a large amount of the circuit’s layout and are very power hungry.